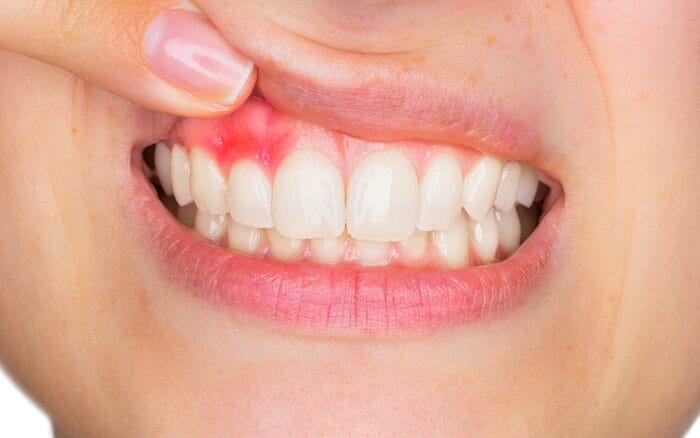
Did you know that nearly half of all adults over the age of 30 suffer from some form of gum disease? That’s right! Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is more common than you might think. But don’t worry, we’ve got you covered with everything you need to know about gingivitis—from what it is and how it develops to how you can prevent and treat it. So, sit back, relax, and let’s dive into the world of healthy gums!
What is Gingivitis?
Definition: Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gums. It’s caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to more serious gum disease (periodontitis) and even tooth loss.
Causes of gingivitis:
- Plaque Buildup: The primary cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of plaque on your teeth. Plaque forms when sugars and starches in food interact with bacteria in your mouth. If not removed through brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, leading to gingivitis.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco products can interfere with gum tissue and make it harder for gums to heal.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can reduce saliva flow, which protects your gums and teeth.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and other immune system disorders can affect your gum health.
How Gingivitis Develops: The process starts with the formation of plaque on your teeth. When plaque is not removed, it can irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation. This inflammation is the first sign of gingivitis. Over time, if plaque and tartar are not removed, the inflammation can worsen, leading to more serious gum disease.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Recognizing the symptoms of gingivitis early can help prevent the progression to more serious gum disease. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Red, Swollen Gums: Healthy gums should be firm and pink. If your gums are red and swollen, it could be a sign of gingivitis.
- Bleeding Gums: Do your gums bleed when you brush or floss? This is a common symptom of gingivitis.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a sign that you have gingivitis.
- Receding Gums: If your gums are pulling away from your teeth, exposing more of the tooth or its root, you might have gingivitis.
When to See a Dentist: If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can prevent gingivitis from progressing to more severe gum disease.
Gingivitis Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing gingivitis:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Skipping brushing and flossing allows plaque to build up and irritate your gums.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: These habits can weaken your immune system and make it harder for your gums to heal.
- Genetics: If gum disease runs in your family, you might be more prone to developing gingivitis.
- Systemic Diseases: Conditions like diabetes can affect your body’s ability to fight infection, including gum infections.
- Medications: Some medications can cause dry mouth, reducing saliva flow and making it easier for plaque to form.
Gingivitis Prevention
The good news is that gingivitis is preventable! Here are some strategies to keep your gums healthy:
- Good Oral Hygiene Practices:
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to brush for at least two minutes each time.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under your gumline.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. Your dentist can remove tartar that brushing and flossing can’t.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help keep your gums healthy. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks, which can contribute to plaque buildup.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products can significantly reduce your risk of developing gingivitis.
- Managing Medical Conditions: If you have diabetes or other systemic diseases, work with your healthcare provider to manage your condition. Good overall health can help maintain healthy gums.
- Using Antibacterial Mouthwash: Incorporating an antibacterial mouthwash into your daily routine can help reduce plaque and prevent gingivitis.
Gingivitis Treatment Options
If you already have gingivitis, don’t worry! There are several effective treatment options:
- Professional Cleaning: Your dentist can perform a deep cleaning, known as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. This can help reduce inflammation and allow your gums to heal.
- Home Care: After professional cleaning, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene at home. Brush and floss regularly and use an antibacterial mouthwash to keep plaque at bay.
- Medications: In some cases, your dentist might prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobial mouthwash to help control infection and inflammation.
- Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular dental visits to monitor your gum health and catch any potential issues early.
Myths and Facts About Gingivitis
Let’s bust some common myths about gingivitis and set the record straight with facts!
- Myth: Bleeding gums are normal. Fact: Bleeding gums are not normal and are a sign of gingivitis or other gum problems.
- Myth: Gingivitis is not a big deal. Fact: If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more serious gum disease that can lead to tooth loss.
- Myth: Brushing hard will remove all plaque. Fact: Brushing too hard can damage your gums and enamel. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle strokes.
- Myth: You only need to see a dentist if you have a toothache. Fact: Regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining overall oral health and preventing issues like gingivitis.
Conclusion
Gingivitis may be common, but it’s also preventable and treatable. By practicing good oral hygiene, eating a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco, and visiting your dentist regularly, you can keep your gums healthy and avoid the complications of gum disease. Remember, healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile!
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gingivitis or have concerns about your gum health, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with your dentist. Early intervention is key to maintaining your oral health.
Additional Resources
For more information on gingivitis and oral health, check out these reputable sources: